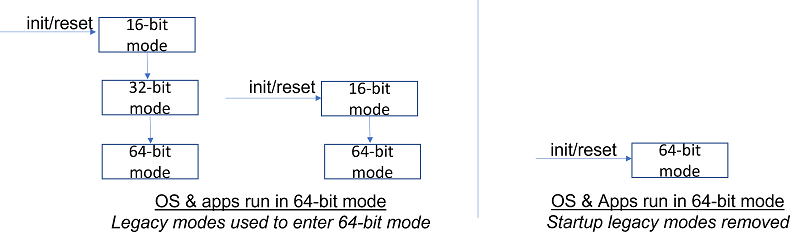
Did you know that even the very latest multicore 64-bit x64 CPUs still boot up in the original 16-bit 8086 mode from 1978? They also support 32-bit modes and this is all for compatibility reasons. Well, Intel thinks it's time to finally get rid of this legacy baggage and has released a document proposing the changes for a 64-bit only future called x86S.
What I'd really like to see, is a 128-bit CPU, the next evolution. However, there's no market for them at the moment, but it would be fascinating to see one, of any architecture. It would have a huge pinout too and a smaller core count for a given process node due to the bigger size of the core.
Full details here:

 www.intel.com
www.intel.com
General info on 128-bit computing:
 en.wikipedia.org
en.wikipedia.org
What I'd really like to see, is a 128-bit CPU, the next evolution. However, there's no market for them at the moment, but it would be fascinating to see one, of any architecture. It would have a huge pinout too and a smaller core count for a given process node due to the bigger size of the core.

What Would Be the Benefits of a 64-bit Mode-Only Architecture?
A 64-bit mode-only architecture removes some older appendages of the architecture, reducing the overall complexity of the software and hardware architecture. By exploring a 64-bit mode-only architecture, other changes that are aligned with modern software deployment could be made. These changes include:
Using the simplified segmentation model of 64-bit for segmentation support for 32-bit applications, matching what modern operating systems already use.
Removing ring 1 and 2 (which are unused by modern software) and obsolete segmentation features like gates.
Removing 16-bit addressing support.
Eliminating support for ring 3 I/O port accesses.
Eliminating string port I/O, which supported an obsolete CPU-driven I/O model.
Limiting local interrupt controller (APIC) use to X2APIC and remove legacy 8259 support.
Removing some unused operating system mode bits.
Full details here:

Envisioning a Simplified Intel® Architecture
Intel investigated architectural enhancements and modifications for a 64-bit mode-only architecture.
General info on 128-bit computing:
